Appearance

雨天擦玻璃
作为 WallPaper Engine(墙裂推荐的一款 steam 动态壁纸软件) 的深度用户,有一张壁纸《Rain Day》我一直非常喜欢,逼真的雨珠顺着玻璃滑落时的折射光斑、鼠标移动时的动态视差…… 这些细节让我总忍不住想:「这么细腻的动态效果,到底是用什么技术实现的?」
直到某天,我偶然发现这款壁纸的技术标签里写着「网页」—— 作为前端开发者,DNA 瞬间动了!右键点击在资源管理器中打开,发现源码早已被打包工具混淆变量名全是a,b,c。但没关系,前端人搞逆向,主打一个拆解重组,在一些工具的辅助并在我秃头式两天两夜的折腾下,终结将几千行的混淆代码从混乱变得有序,并在我完全理解源代码逻辑后,新增了一个有趣(无聊)的功能——擦玻璃效果。
先看看效果:点击查看效果
项目结构
经过我的整理和重组,将代码用 TypeScript + ES6 Class 重新实现,代码结构如下:
plaintext
rainDay/
├─ img/ # 纹理图片
| ├─ drop-alpha.png
| ├─ drop-color.png
| ├─ texture-rain-bg.png
| ├─ texture-rain-fg.png
├─ shaders/ # shader文件
| ├─ simpleVert.glsl
| ├─ waterFrag.glsl
├─ types/ # ts类型文件
| ├─ index.ts
├─ utils/ # 工具函数文件
| ├─ index.ts
├─ index.vue # 主页面
├─ RainDrops.ts # 雨滴类
├─ RainRenderer.ts # 场景类
├─ webgl.ts # webgl封装
├─ WebGlContext.ts # webgl环境类核心逻辑
实现雨滴效果的核心逻辑:
plaintext
RainRenderer更新纹理 → Raindrops生成新雨滴 → WebGL渲染(雨滴Canvas+纹理叠加)RainRenderer类
RainRenderer类主要负责将雨滴动态数据(由 Raindrops 生成的画布内容)与背景纹理、光泽纹理结合,通过着色器计算折射、阴影、光泽等效果,最终在主画布上渲染出动态、真实的雨水视觉效果,其核心功能包括:
- WebGL 初始化与配置:创建 WebGL 上下文,加载顶点 / 片段着色器,配置渲染参数(如折射范围、亮度、透明度等)。
- 纹理管理:绑定光泽、前景、背景等纹理,并支持动态更新纹理(如切换天气或背景时)。
- 视差效果处理:通过鼠标移动参数(parallaxX/parallaxY)增强画面立体感。
- 动态渲染循环:通过 requestAnimationFrame 实现实时渲染,持续将雨滴动态画布内容与纹理融合输出。
以下是RainRenderder的代码实现:
点击查看代码
typescript
import GL from "./WebGLContext";
import { createCanvas } from "./utils";
import vertShader from "./shaders/simpleVert.glsl?raw";
import fragShader from "./shaders/waterFrag.glsl?raw";
import { IRendererOptions } from "./types";
// 默认渲染配置
const defaultOptions = {
renderShadow: false, // 是否渲染阴影
minRefraction: 256, // 最小折射强度(控制纹理扭曲程度)
maxRefraction: 512, // 最大折射强度
brightness: 1, // 整体亮度系数
alphaMultiply: 20, // 透明度乘法系数(控制雨滴透明度)
alphaSubtract: 5, // 透明度减法系数
parallaxBg: 5, // 背景视差强度(鼠标移动时背景偏移量)
parallaxFg: 20 // 前景视差强度(鼠标移动时前景偏移量)
};
/**
* 雨水效果渲染核心类
* 负责将雨滴动态(canvasLiquid)与前景/背景纹理融合,通过WebGL实现实时渲染
*/
export default class RainRenderer {
canvas: HTMLCanvasElement; // 最终输出画面的主画布
canvasLiquid: HTMLCanvasElement | null; // 雨滴动态数据画布(由Raindrops生成动态雨滴纹理)
imageFg: HTMLCanvasElement | null; // 前景纹理(叠加在雨滴上方的静态图像)
imageBg: HTMLCanvasElement | null; // 背景纹理(雨滴下方的静态背景图像)
imageShine: HTMLCanvasElement | null; // 光泽纹理(可选,增强雨滴反光效果)
textures: Array<{ name: string, img: HTMLCanvasElement }> = []; // 纹理列表
options: IRendererOptions;
gl: GL;
width: number = 0;
height: number = 0;
programWater: WebGLProgram | null; // 水效果渲染程序
parallaxX: number = 0; // X轴视差值 (没做视差处理)
parallaxY: number = 0; // Y轴视差值 (没做视差处理)
rafId: number | null = null;
constructor(
canvas: HTMLCanvasElement,
canvasLiquid: HTMLCanvasElement,
imageFg: HTMLCanvasElement,
imageBg: HTMLCanvasElement,
imageShine: HTMLCanvasElement | null,
options = {}
) {
this.canvas = canvas;
this.canvasLiquid = canvasLiquid;
this.imageShine = imageShine;
this.imageFg = imageFg;
this.imageBg = imageBg;
this.options = Object.assign({}, defaultOptions, options);
this.width = this.canvas.width;
this.height = this.canvas.height;
this.gl = new GL(this.canvas, { alpha: false }, vertShader, fragShader);
this.programWater = this.gl.program;
this.init();
}
init() {
const { gl } = this;
// 向着色器传递关键Uniform变量(GPU可访问的全局变量)
gl.createUniform("2f", "resolution", this.width, this.height); // 主画布分辨率
gl.createUniform("1f", "textureRatio", this.imageBg!.width / this.imageBg!.height); // 背景纹理宽高比
gl.createUniform("1i", "renderShine", this.imageShine != null); // 是否启用光泽纹理
gl.createUniform("1i", "renderShadow", this.options.renderShadow); // 是否渲染阴影
gl.createUniform("1f", "minRefraction", this.options.minRefraction); // 最小折射强度
gl.createUniform("1f", "refractionDelta", this.options.maxRefraction - this.options.minRefraction); // 折射强度范围
gl.createUniform("1f", "brightness", this.options.brightness); // 亮度
gl.createUniform("1f", "alphaMultiply", this.options.alphaMultiply); // 透明度乘法系数(控制雨滴透明度)
gl.createUniform("1f", "alphaSubtract", this.options.alphaSubtract); // 透明度减法系数
gl.createUniform("1f", "parallaxBg", this.options.parallaxBg); // 背景视差强度(鼠标移动时背景偏移量)
gl.createUniform("1f", "parallaxFg", this.options.parallaxFg); // 前景视差强度
// 纹理单元0
gl.createTexture(null, 0);
// 光泽、前景、背景纹理绑定到纹理单元1,2,3
this.textures = [
// 无光泽纹理时用2x2空画布避免着色器报错
{ name: 'textureShine', img: this.imageShine == null ? createCanvas(2, 2) : this.imageShine },
{ name: 'textureFg', img: this.imageFg! }, // 前景纹理
{ name: 'textureBg', img: this.imageBg! } // 背景纹理
];
//每个纹理创建WebGL纹理对象,绑定到着色器对应的Uniform变量
this.textures.forEach((texture, i) => {
gl.createTexture(texture.img, i + 1); // 纹理单元1/2/3分别对应三个纹理
gl.createUniform('1i', texture.name, i + 1); // 告诉着色器该纹理使用的单元位置
});
this.draw();
}
draw() {
const { gl, programWater } = this;
if (!programWater) return;
// 激活水效果渲染程序
gl.useProgram(programWater);
// 更新视差参数
gl.createUniform("2f", "parallax", this.parallaxX, this.parallaxY);
// 更新雨滴动态纹理
this.updateTexture();
// 绘制
gl.draw();
this.rafId = requestAnimationFrame(this.draw.bind(this));
}
updateTexture() {
this.gl.activeTexture(0); // 激活纹理单元0
this.gl.updateTexture(this.canvasLiquid!); // 将canvasLiquid的内容更新到纹理
}
updateTextures() {
this.textures.forEach((texture, i) => {
this.gl.activeTexture(i + 1); // 激活对应纹理单元
this.gl.updateTexture(texture.img); // 更新纹理内容
});
}
destroy() {
this.gl.destroy(); // 销毁WebGL上下文(释放着色器、纹理等资源)
if (this.rafId) {
cancelAnimationFrame(this.rafId); // 停止动画循环
this.rafId = null;
}
// 清空纹理和画布引用(帮助垃圾回收)
this.textures = [];
this.canvasLiquid = null;
this.imageFg = null;
this.imageBg = null;
this.imageShine = null;
}
}RainDrop类
RainDrop类主要负责动态雨滴效果生成,动态产出雨水纹理: 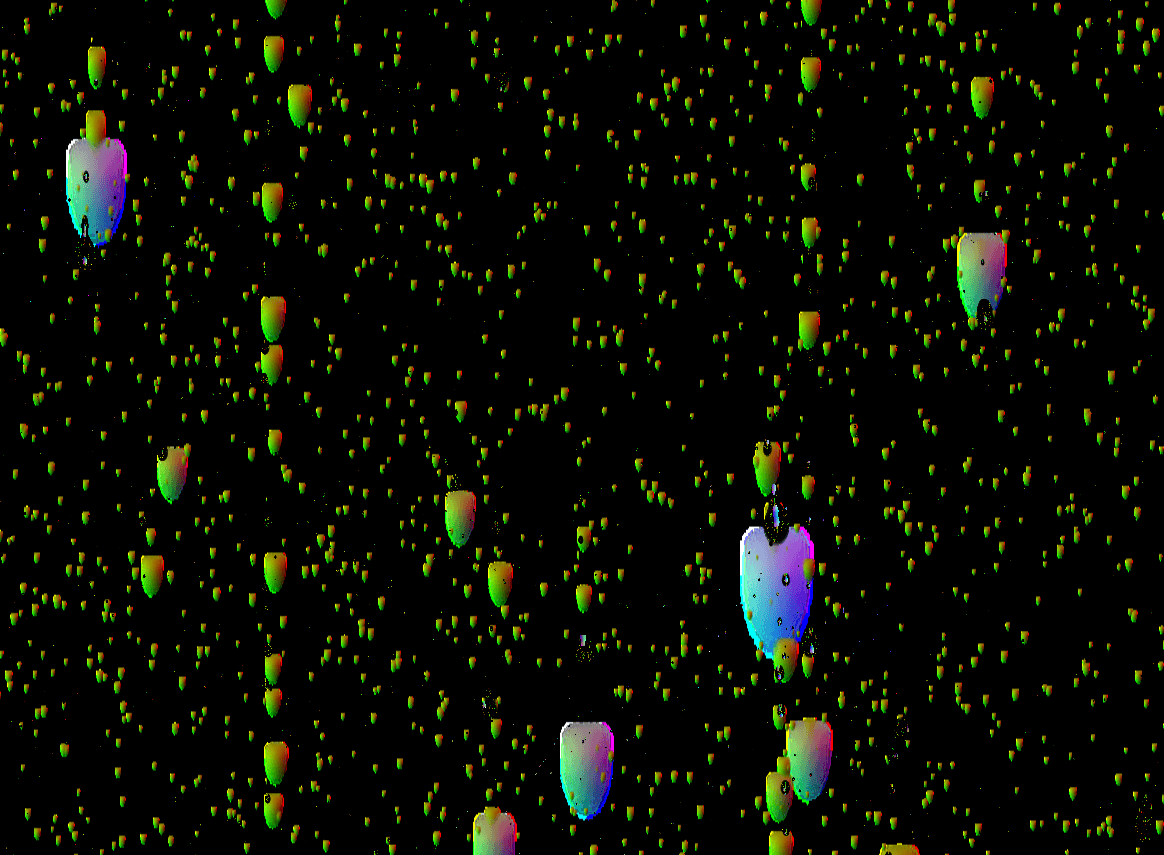 其核心逻辑如下:
其核心逻辑如下:
- 雨滴状态管理 通过 drops 数组维护所有活跃的雨滴,每个雨滴对象包含位置、大小、动量等关键属性,通过 updateDrops 方法更新状态(如下落、碰撞、收缩消亡)。
- 动态生成与消亡 生成:在 updateRain 中基于概率生成新雨滴,位置限定在 spawnArea 区域内(如从顶部下落)。 消亡:通过 shrink 属性控制半径缩小,当半径 ≤0 时标记为 killed,后续被过滤回收。
- 碰撞检测 检测雨滴间的距离,若小于碰撞半径则合并(如大雨滴吸收小水滴,调整动量和大小)。
- 纹理绘制
- 预生成 dropsGfx 数组(255 种不同深度的雨滴纹理),通过叠加颜色(dropColor)、透明度(dropAlpha)和深度(蓝色通道)模拟立体感。
- drawDrop 方法根据雨滴大小和扩散程度选择对应纹理,绘制到画布。
- 微小水滴效果 通过 droplets 画布绘制更细腻的小水滴,updateDroplets 方法控制其生成速率和清理(如通过 destination-out 混合模式擦除旧水滴
以下是RainDrop类的代码实现:
点击查看代码
typescript
import {Drop, RaindropsOptions} from "./types";
import {chance, random, times, createCanvas} from "./utils";
const defaultRaindropsOptions: RaindropsOptions = {
minR: 10,
maxR: 40,
maxDrops: 900,
rainChance: 0.3,
rainLimit: 3,
dropletsRate: 50,
dropletsSize: [2, 4],
dropletsCleaningRadiusMultiplier: 0.43,
raining: true,
globalTimeScale: 1,
trailRate: 1,
autoShrink: true,
spawnArea: [-0.1, 0.95],
trailScaleRange: [0.2, 0.5],
collisionRadius: 0.65,
collisionRadiusIncrease: 0.01,
dropFallMultiplier: 1,
collisionBoostMultiplier: 0.05,
collisionBoost: 1,
};
const initDrop: Drop = {
x: 0,
y: 0,
r: 0,
spreadX: 0,
spreadY: 0,
momentum: 0,
momentumX: 0,
trailProgress: 0,
trailThreshold: 0,
parent: null,
isNew: true,
killed: false,
shrink: 0,
}
export default class RainDrops {
private readonly width: number;
private readonly height: number;
private readonly scale: number;
private readonly dropColorTexture: HTMLImageElement;
private readonly dropAlphaTexture: HTMLImageElement;
canvas: HTMLCanvasElement;
private ctx: CanvasRenderingContext2D;
//水痕扩散画布
private droplets: HTMLCanvasElement;
private dropletsCtx: CanvasRenderingContext2D;
//活跃雨滴对象数组
private drops: Drop[] = [];
//预渲染雨滴图形缓存
private dropsGfx: HTMLCanvasElement[] = [];
//水痕清除画笔(圆形遮罩,用于模拟水痕消失)
private clearDropletsGfx: HTMLCanvasElement | null = null;
private dropletsCounter: number = 0;
private dropletsPixelDensity: number = 1;
private textureCleaningIterations: number = 0;
private lastRender: number = 0;
// 雨滴配置
private readonly options: RaindropsOptions;
private rafId: number | null = null;
constructor(
width: number,
height: number,
scale: number,
dropAlphaTexture: HTMLImageElement,
dropColorTexture: HTMLImageElement,
options?: Partial<RaindropsOptions>
) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
this.scale = scale;
this.dropAlphaTexture = dropAlphaTexture;
this.dropColorTexture = dropColorTexture;
this.options = Object.assign({}, defaultRaindropsOptions, options);
// 初始化画布系统
this.canvas = createCanvas(this.width, this.height);
this.ctx = this.canvas.getContext('2d')!;
// this.ctx.imageSmoothingQuality = 'high'; // 优化图像平滑度
const density = this.dropletsPixelDensity;
this.droplets = createCanvas(this.width * density, this.height * density);
this.dropletsCtx = this.droplets.getContext('2d')!;
// this.dropletsCtx.fillStyle = '#000'; // 初始化为黑色背景
// 预渲染雨滴图形资源
this.renderDropGraphics();
// 启动动画循环
this.update();
}
get deltaR() {
return this.options.maxR - this.options.minR;
}
get area() {
return (this.width * this.height) / this.scale;
}
get areaMultiplier() {
return Math.sqrt(this.area / (1024 * 768));
}
/**
* 预渲染不同透明度的雨滴图形
* 预计算雨滴的图形和水痕清除工具,避免在动画循环中重复计算,从而提升性能
* 通过分离预渲染和实时绘制,确保了雨滴动画的流畅性
*/
private renderDropGraphics() {
// 雨滴基础尺寸
const dropSize = 64
const dropBuffer = createCanvas(dropSize, dropSize);
const dropBufferCtx = dropBuffer.getContext('2d')!;
// 生成不同透明度的雨滴图形
this.dropsGfx = Array.from({length: 255}, (_, index) => {
const drop = createCanvas(dropSize, dropSize);
const dropCtx = drop.getContext('2d')!;
dropBufferCtx.clearRect(0, 0, dropSize, dropSize);
// 1. 绘制基础颜色层(使用预设的 dropColor 纹理)
dropBufferCtx.globalCompositeOperation = "source-over"; // 合成模式:覆盖(默认)
dropBufferCtx.drawImage(this.dropColorTexture, 0, 0, dropSize, dropSize); // 绘制颜色纹理
dropBufferCtx.globalCompositeOperation = 'screen' // 合成模式:滤色(变亮,叠加蓝色)
dropBufferCtx.fillStyle = `rgba(0, 0, ${index}, 1)`; // 蓝色通道随 i 增大(0→254)
dropBufferCtx.fillRect(0, 0, dropSize, dropSize); // 填充蓝色层
// 2. 应用透明度遮罩(通过 alpha 纹理控制形状)
dropCtx.globalCompositeOperation = "source-over"; // 合成模式:覆盖
dropCtx.drawImage(this.dropAlphaTexture, 0, 0, dropSize, dropSize); // 绘制透明度纹理(形状)
dropCtx.globalCompositeOperation = 'source-in'; // 合成模式:仅保留重叠部分(形状裁剪)
dropCtx.drawImage(dropBuffer, 0, 0, dropSize, dropSize); // 将临时画布内容裁剪为透明度形状
return drop
})
// 初始化水痕清除画笔(圆形遮罩)
this.clearDropletsGfx = createCanvas(128, 128)
const clearCtx = this.clearDropletsGfx.getContext('2d')!;
clearCtx.fillStyle = '#000'
clearCtx.beginPath()
clearCtx.arc(64, 64, 64, 0, Math.PI * 2)
clearCtx.fill()
}
private clearCanvas() {
this.ctx.clearRect(0, 0, this.width, this.height);
}
private drawDroplet(x: number, y: number, r: number) {
this.drawDrop(this.dropletsCtx, Object.assign(Object.create(initDrop), {
x: x * this.dropletsPixelDensity,
y: y * this.dropletsPixelDensity,
r: r * this.dropletsPixelDensity
}))
}
private drawDrop(ctx: CanvasRenderingContext2D, drop: Drop) {
if (this.dropsGfx.length > 0) {
let x = drop.x
let y = drop.y
let r = drop.r
let spreadX = drop.spreadX
let spreadY = drop.spreadY
let scaleX = 1
let scaleY = 1.5
// 将半径增量归一化为 0~1 的数值, * 0.9将范围缩小为 0~0.9避免取到 dropsGfx 数组的最大索引,预留边界
let d = Math.max(0, Math.min(1, ((r - this.options.minR) / (this.deltaR)) * 0.9));
// 扩展程度越大,分母越大,整个分数越小,因为dropsGfx存储的雨滴缓存,下标越大,越清晰
d *= 1 / (((drop.spreadX + drop.spreadY) * 0.5) + 1);
ctx.globalAlpha = 1;
ctx.globalCompositeOperation = "source-over"; // 合成模式设为“正常覆盖”(新图形覆盖旧内容)
// 将 d 转换为 `dropsGfx` 的数组索引(0 到数组长度-1)
d = Math.floor(d * (this.dropsGfx.length - 1));
ctx.drawImage(this.dropsGfx[d],
// 绘制位置(x 方向):雨滴中心 x 坐标减去横向扩展后的半径,再乘以整体缩放 `this.scale`
(x - (r * scaleX * (spreadX + 1))) * this.scale,
// 绘制位置(y 方向):雨滴中心 y 坐标减去纵向扩展后的半径,再乘以整体缩放 `this.scale`
(y - (r * scaleY * (spreadY + 1))) * this.scale,
// 绘制宽度:横向扩展后的直径(2r)乘以缩放因子和整体缩放
(r * 2 * scaleX * (spreadX + 1)) * this.scale,
// 绘制高度:纵向扩展后的直径(2r)乘以缩放因子和整体缩放
(r * 2 * scaleY * (spreadY + 1)) * this.scale
)
}
}
// 小水滴的清理、生成和最终渲染
private updateDroplets(timeScale: number) {
// 纹理清理剩余次数大于0执行清理
if (this.textureCleaningIterations > 0) {
this.textureCleaningIterations -= timeScale;
this.dropletsCtx.globalCompositeOperation = 'destination-out'; // 合成模式:擦除目标区域
this.dropletsCtx.fillStyle = `rgba(0, 0, 0, ${0.05 * timeScale})`;
this.dropletsCtx.fillRect(0, 0, this.width * this.dropletsPixelDensity, this.height * this.dropletsPixelDensity);
}
if (this.options.raining) {
this.dropletsCounter += this.options.dropletsRate * timeScale * this.areaMultiplier //累计生成计数器(速率×时间×区域乘数)
times(this.dropletsCounter, (i) => {
this.dropletsCounter--
this.drawDroplet(
random(this.width / this.scale),
random(this.height / this.scale),
random(this.options.dropletsSize[0], this.options.dropletsSize[1], (n) => {
return n * n;// 大小:从[2,4]中随机(通过n²调整概率,小尺寸更常见)
})
)
})
}
this.ctx.drawImage(this.droplets, 0, 0, this.width, this.height);
}
clearDroplets(x: number, y: number, r = 30) {
let ctx = this.dropletsCtx;
ctx.globalCompositeOperation = "destination-out";
ctx.drawImage(
this.clearDropletsGfx!,
(x - r) * this.dropletsPixelDensity * this.scale,
(y - r) * this.dropletsPixelDensity * this.scale,
(r * 2) * this.dropletsPixelDensity * this.scale,
(r * 2) * this.dropletsPixelDensity * this.scale * 1.5
)
}
eraseDroplets(x: number, y: number, w: number, h: number) {
let ctx = this.dropletsCtx;
ctx.globalCompositeOperation = "destination-out";
ctx.fillRect(x, y, w, h);
this.drops.forEach(drop => {
if (drop.x * this.scale > x
&& drop.x * this.scale < x + w
&& drop.y * this.scale > y
&& drop.y * this.scale < y + h) {
drop.killed = true
}
})
}
createDrop(options: Drop): Drop | null {
if (this.drops.length >= this.options.maxDrops * this.areaMultiplier) return null;
return Object.assign(Object.create(initDrop), options);
}
addDrop(drop: Drop) {
if (this.drops.length >= this.options.maxDrops * this.areaMultiplier || drop == null) return false;
this.drops.push(drop);
return true;
}
clearDrops() {
this.drops.forEach((drop) => {
setTimeout(() => {
drop.shrink = 0.1 + (random(0.5));
}, random(1200))
})
this.clearTexture();
}
clearTexture() {
this.textureCleaningIterations = 50;
}
private updateRain(timeScale: number) {
let rainDrops = [];
if (this.options.raining) {
let limit = this.options.rainLimit * timeScale * this.areaMultiplier
let count = 0
while (chance(this.options.rainChance * timeScale * this.areaMultiplier) && count < limit) {
count++
let r = random(this.options.minR, this.options.maxR, (n) => {
return Math.pow(n, 3);
// 用于调整雨滴半径的概率分布,使较大的雨滴半径更易被选中
// 当 n=10(最小半径)时,权重为 10³=1000;
// 当 n=20 时,权重为 20³=8000(是 n=10 的 8 倍);
// 当 n=40(最大半径)时,权重为 40³=64000(是 n=10 的 64 倍)。
// 因此,较大的半径值会被更频繁地生成,使雨滴效果更偏向于大尺寸雨滴。
});
let rainDrop = this.createDrop(Object.assign(Object.create(initDrop), {
x: random(this.width / this.scale),
y: random((this.height / this.scale) * this.options.spawnArea[0], (this.height / this.scale) * this.options.spawnArea[1]),
r,
momentum: 1 + ((r - this.options.minR) * 0.1) + random(2),
spreadX: 1.5,
spreadY: 1.5
}));
if (rainDrop != null) {
rainDrops.push(rainDrop);
}
}
}
return rainDrops;
}
// 雨滴动画的状态更新核心,负责处理雨滴的生成、移动、碰撞、消亡等全生命周期管理
private updateDrops(timeScale: number) {
let newDrops: Drop[] = [] // 存储本帧存活的雨滴
this.updateDroplets(timeScale)
let rainDrops = this.updateRain(timeScale)
newDrops = newDrops.concat(rainDrops);
// 将存活的雨滴按照y轴坐标从小到大排序 +a.x/+b.x 是为什么确保相同y坐标根据x坐标从小到大排序
this.drops.sort((a, b) => {
let va = (a.y * (this.width / this.scale)) + a.x;
let vb = (b.y * (this.width / this.scale)) + b.x;
return va > vb ? 1 : va == vb ? 0 : -1;
})
this.drops.forEach((drop, i) => {
if (!drop.killed) {
// 雨滴 “缓慢下落” 的概率控制 (drop.r - 最小半径调整值) * (0.1 / 半径范围差) * 时间缩放
// 0.1 / this.deltaR 的本质是归一化处理,通过将雨滴半径的绝对差值除以半径范围(deltaR),抵消了 maxR 和 minR 配置差异对概率的影响,
// 使得无论雨滴的大小范围如何设置,“缓慢下落” 的触发概率始终保持在合理的相对水平,最终让雨滴的动态行为更自然、稳定
if (chance((drop.r - (this.options.minR * this.options.dropFallMultiplier)) * (0.1 / this.deltaR) * timeScale)) {
// 雨滴的动量(momentum)会增加一个随机值((drop.r / maxR) * 4)
drop.momentum += random((drop.r / this.options.maxR) * 4);
}
// 小尺寸雨滴的自动收缩
if (this.options.autoShrink && drop.r <= this.options.minR && chance(0.05 * timeScale)) {
drop.shrink += 0.01;
}
drop.r -= drop.shrink * timeScale;
if (drop.r <= 0) drop.killed = true;
//生成拖尾
if (this.options.raining) {
// 记录一个进度值,用于判断是否生成拖尾,可以理解为,速度越大,越容易生成
drop.trailProgress += drop.momentum * timeScale * this.options.trailRate;
if (drop.trailProgress > drop.trailThreshold) {
let trailDrop = this.createDrop(Object.assign(Object.create(initDrop), {
x: drop.x + (random(-drop.r, drop.r) * 0.1),
y: drop.y - (drop.r * 0.01),
r: drop.r * random(...this.options.trailScaleRange),
spreadY: drop.momentum * 0.1,
parent: drop
}));
if (trailDrop != null) {
newDrops.push(trailDrop);
drop.r *= Math.pow(0.97, timeScale);
drop.trailProgress = 0;
drop.trailThreshold = random(this.options.minR, this.options.maxR) - (drop.momentum * 2 * this.options.trailRate) + (this.options.maxR - drop.r);
}
}
}
//规格化散布
drop.spreadX *= Math.pow(0.4, timeScale);
drop.spreadY *= Math.pow(0.7, timeScale);
//更新位置
let moved = drop.momentum > 0;
if (moved && !drop.killed) {
drop.y += drop.momentum * this.options.globalTimeScale;
drop.x += drop.momentumX * this.options.globalTimeScale;
if (drop.y > (this.height / this.scale) + drop.r) {
drop.killed = true;
}
}
// 检查碰撞
let checkCollision = (moved || drop.isNew) && !drop.killed;
drop.isNew = false;
if (checkCollision) {
// 只遍历70个,避免全量遍历所有雨滴,优化性能
this.drops.slice(i + 1, i + 70).forEach((drop2) => {
//basic check
if (
drop != drop2 &&
drop.r > drop2.r &&
drop.parent != drop2 &&
drop2.parent != drop &&
!drop2.killed
) {
let dx = drop2.x - drop.x;
let dy = drop2.y - drop.y;
let d = Math.sqrt((dx * dx) + (dy * dy));
// 当两雨滴的实际距离 d 小于此阈值时判定为碰撞
// drop.momentum * this.options.collisionRadiusIncrease * timeScale 表示动量越大、时间缩放系数越高,碰撞范围越大
if (d < (drop.r + drop2.r) * (this.options.collisionRadius + (drop.momentum * this.options.collisionRadiusIncrease * timeScale))) {
let pi = Math.PI;
let r1 = drop.r;
let r2 = drop2.r;
let a1 = pi * (r1 * r1);
let a2 = pi * (r2 * r2);
let targetR = Math.sqrt((a1 + (a2 * 0.8)) / pi); // 合并后的半径
if (targetR > this.options.maxR) {
targetR = this.options.maxR;
}
drop.r = targetR;
drop.momentumX += dx * 0.1; // 根据碰撞方向调整水平动量
drop.spreadX = 0;
drop.spreadY = 0;
drop2.killed = true;
// 新动量(取较大值,且不超过 40)
drop.momentum = Math.max(drop2.momentum, Math.min(40, drop.momentum + (targetR * this.options.collisionBoostMultiplier) + this.options.collisionBoost));
}
}
});
}
//放慢动量
drop.momentum -= Math.max(1, (this.options.minR * 0.5) - drop.momentum) * 0.1 * timeScale;
if (drop.momentum < 0) drop.momentum = 0;
drop.momentumX *= Math.pow(0.7, timeScale);
if (!drop.killed) {
newDrops.push(drop);
if (moved && this.options.dropletsRate > 0) this.clearDroplets(drop.x, drop.y, drop.r * this.options.dropletsCleaningRadiusMultiplier);
this.drawDrop(this.ctx, drop);
}
}
}, this)
this.drops = newDrops;
}
private update() {
this.clearCanvas()
let now = Date.now();
if (!this.lastRender) this.lastRender = now;
// 计算时间缩放因子(用于平衡不同帧率下的动画速度)
const delta = now - this.lastRender;
let timeScale = delta / ((1 / 60) * 1000); // // 理想60帧的单帧时间约16.666ms,timeScale = 实际时间差 / 理想单帧时间
if (timeScale > 1.1) timeScale = 1.1 //防止帧率过低时动画加速过快
timeScale *= this.options.globalTimeScale //用户可配置的动画速度
this.lastRender = now;
this.updateDrops(timeScale)
this.rafId = requestAnimationFrame(this.update.bind(this));
}
destroy() {
if (this.rafId) {
cancelAnimationFrame(this.rafId);
this.rafId = null;
}
this.drops = [];
}
}着色器
片段着色器waterFrag.glsl是能够实现逼真物理效果的重要部分, 该着色器用于渲染水雨滴效果,核心功能包括:
- 模拟水面或雨滴的折射扭曲(通过背景纹理的偏移采样)
- 叠加前景/背景天气纹理(如雨水、阳光等)
- 计算高光反射(模拟水滴的光泽)
- 处理视差效果(鼠标移动时前景/背景的相对偏移)
- 控制整体亮度、透明度和阴影(增强真实感) 其代码如下:
点击查看代码
text
precision mediump float;
// ---------------------------
// Uniform 变量(由 CPU 传递的全局参数)
// ---------------------------
uniform sampler2D u_waterMap; // 动态水纹/雨滴纹理(由 raindrops.js 生成)
uniform sampler2D u_textureShine; // 高光纹理(模拟水滴反光)
uniform sampler2D u_textureFg; // 前景纹理(如雨水、雾气等前景层)
uniform sampler2D u_textureBg; // 背景纹理(如天空、云层等背景层)
// 顶点着色器传递的纹理坐标
varying vec2 v_texCoord;
// 画布相关参数
uniform vec2 u_resolution; // 画布分辨率(宽, 高)
uniform vec2 u_parallax; // 鼠标移动产生的视差偏移量(x, y)
uniform float u_parallaxFg; // 前景视差强度(偏移幅度)
uniform float u_parallaxBg; // 背景视差强度(偏移幅度)
uniform float u_textureRatio; // 背景纹理宽高比(用于适配画布)
// 渲染开关
uniform bool u_renderShine; // 是否启用高光效果
uniform bool u_renderShadow; // 是否启用阴影效果
// 视觉参数
uniform float u_minRefraction; // 最小折射强度(背景扭曲最小偏移量)
uniform float u_refractionDelta; // 折射强度范围(最大 - 最小)
uniform float u_brightness; // 整体亮度系数
uniform float u_alphaMultiply; // 透明度乘法因子
uniform float u_alphaSubtract; // 透明度减法因子
// ---------------------------
// 辅助函数
// ---------------------------
/**
* 颜色混合函数:基于透明度混合前景与背景色
* @param bg 背景颜色
* @param fg 前景颜色
* @return 混合后的颜色(包含透明度)
*/
vec4 blend(vec4 bg, vec4 fg) {
vec3 bgm = bg.rgb * bg.a; // 背景色按透明度加权
vec3 fgm = fg.rgb * fg.a; // 前景色按透明度加权
float ia = 1.0 - fg.a; // 背景剩余可见度
float a = fg.a + bg.a * ia; // 最终透明度
vec3 rgb = (fgm + bgm * ia) / a; // 按透明度归一化混合色
return vec4(rgb, a);
}
/**
* 获取单个像素的纹理坐标增量
* @return 像素尺寸(1/分辨率)
*/
vec2 pixel() {
return vec2(1.0, 1.0) / u_resolution;
}
/**
* 计算视差偏移量
* @param v 视差强度(控制偏移幅度)
* @return 视差偏移的纹理坐标
*/
vec2 parallax(float v) {
return u_parallax * pixel() * v; // 视差 = 鼠标偏移 * 像素尺寸 * 强度
}
/**
* 获取修正后的背景纹理坐标(适配画布宽高比)
* @return 缩放后的纹理坐标(避免拉伸变形)
*/
vec2 scaledTexCoord() {
float ratio = u_resolution.x / u_resolution.y; // 画布宽高比
float ratioDelta = ratio - u_textureRatio; // 画布与纹理宽高比差异
vec2 scale = vec2(1.0);
vec2 offset = vec2(0.0);
if (ratioDelta >= 0.0) {
// 画布更宽:垂直方向缩放并居中
scale.y = 1.0 + ratioDelta;
offset.y = ratioDelta / 2.0;
} else {
// 画布更高:水平方向缩放并居中
scale.x = 1.0 - ratioDelta;
offset.x = -ratioDelta / 2.0;
}
// 转换为标准化纹理坐标并应用缩放/偏移
return (gl_FragCoord.xy / u_resolution + offset) / scale;
}
/**
* 采样水纹纹理(包含视差偏移)
* @param dx 水平偏移量(像素)
* @param dy 垂直偏移量(像素)
* @return 水纹纹理颜色(包含位置、厚度、透明度信息)
*/
vec4 fgColor(float dx, float dy) {
float p2 = u_parallaxFg * 2.0; // 前景视差扩展范围
vec2 scale = vec2(
(u_resolution.x + p2) / u_resolution.x, // 水平缩放(适配视差偏移)
(u_resolution.y + p2) / u_resolution.y // 垂直缩放(适配视差偏移)
);
vec2 scaledTex = gl_FragCoord.xy / u_resolution / scale; // 缩放后的纹理坐标
vec2 offset = vec2(
(1.0 - 1.0/scale.x)/2.0, // 水平居中偏移
(1.0 - 1.0/scale.y)/2.0 // 垂直居中偏移
);
// 采样水纹纹理(添加像素偏移和视差)
return texture2D(u_waterMap, scaledTex + offset + pixel()*vec2(dx, dy) + parallax(u_parallaxFg));
}
// ---------------------------
// 主渲染逻辑
// ---------------------------
void main() {
// 1. 采样背景纹理(应用背景视差偏移)
vec4 bg = texture2D(u_textureBg, scaledTexCoord() + parallax(u_parallaxBg));
// 2. 获取当前像素的水纹数据(位置、厚度、透明度)
vec4 cur = fgColor(0.0, 0.0); // 采样当前像素的水纹纹理
float d = cur.b; // 水纹厚度(影响折射强度)
float x = cur.g; // 水纹 X 方向偏移量(0~1)
float y = cur.r; // 水纹 Y 方向偏移量(0~1)
float a = clamp(cur.a * u_alphaMultiply - u_alphaSubtract, 0.0, 1.0); // 计算最终透明度
// 3. 计算折射偏移(模拟水纹扭曲背景)
vec2 refraction = (vec2(x, y) - 0.5) * 2.0; // 将偏移量转换为 [-1, 1] 范围(表示扭曲方向)
vec2 refractionParallax = parallax(u_parallaxBg - u_parallaxFg); // 视差补偿(前景与背景的偏移差)
// 计算折射后的前景纹理坐标(背景坐标 + 折射偏移 + 视差补偿)
vec2 refractionPos = scaledTexCoord()
+ refraction * (u_minRefraction + d * u_refractionDelta) * pixel() // 折射偏移 = 方向 * 强度 * 像素尺寸
+ refractionParallax;
// 4. 采样前景纹理(带折射效果)
vec4 tex = texture2D(u_textureFg, refractionPos);
// 5. 渲染高光(如果启用)
if (u_renderShine) {
float maxShine = 490.0; // 最大高光强度
float minShine = maxShine * 0.18; // 最小高光强度
// 高光位置:基于水纹扭曲方向和厚度(厚度越大,高光越靠中心)
vec2 shinePos = vec2(0.5, 0.5) + refraction * (-(minShine + (maxShine - minShine) * d) / 512.0);
vec4 shine = texture2D(u_textureShine, shinePos); // 采样高光纹理
tex = blend(tex, shine); // 叠加高光到前景
}
// 6. 渲染阴影(如果启用)
if (u_renderShadow) {
// 采样水纹下方区域的透明度(模拟阴影)
float borderAlpha = fgColor(0.0, -d * 6.0).a;
borderAlpha = clamp(borderAlpha * u_alphaMultiply - (u_alphaSubtract + 0.5), 0.0, 1.0);
borderAlpha *= 0.2; // 削弱阴影强度
vec4 border = vec4(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, borderAlpha); // 纯黑色阴影
tex = blend(border, tex); // 叠加阴影到前景
}
// 7. 最终颜色混合(前景与背景按透明度混合)
gl_FragColor = blend(bg, vec4(tex.rgb * u_brightness, a));
}总结
一些重要步骤在上面代码中注释出来了,其他次要代码我就不一一列出来了。
这次重构让我明白:原来 WebGL + Canvas 还能这样用,还让我深刻理解到,知识是无法掌握不完的,我对前端领域的探索微不足道。另外,通过逆向《Rain Day》,我不仅还原了喜欢的壁纸,还深入理解了图形交互的底层逻辑 —— 这种从0到1的掌控感,比单纯使用壁纸更令人兴奋。
源码已上传代码托管平台,如果有想也研究研究的小伙伴可以做参考:rainDay